Dialogflow and Firebase: Working with Database
If a chatbot accepts data from users, where should this data be stored? And what if you need to implement data reading (for example, a list of products) and display them nicely in a messenger? In both cases, you can't do without a database.
You could try to get by with Google Sheets or a text file, but I would recommend connecting a full-fledged database. Don't think it's complicated. Not at all. Any employee can maintain the database (edit data there), and you'll get tremendous advantages. First, it's the speed of operation (read-write process). Second, you can connect a mobile app, website, or simply use the database simultaneously on multiple devices by different people (your company's employees).
You can use any database. Dialogflow works great with both Airtable and complex DBMS like MySQL.
Getting Started with Firebase
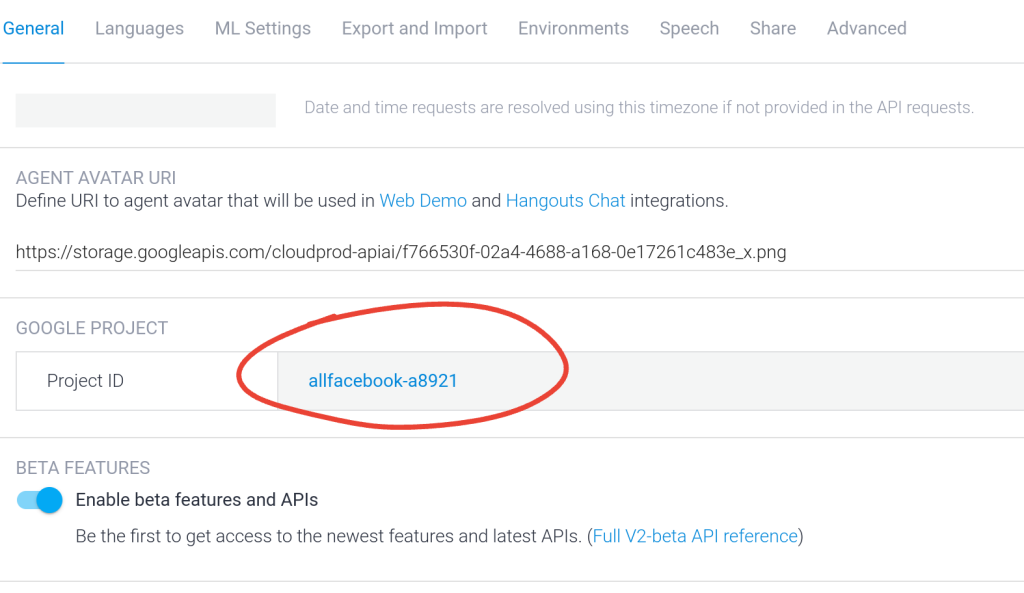
Open the Cloud Firebase console at https://console.firebase.google.com, go to Firestore Database and select the Google Cloud project that was previously created in Dialogflow. Check the name in the Dialogflow agent settings to avoid mistakes.
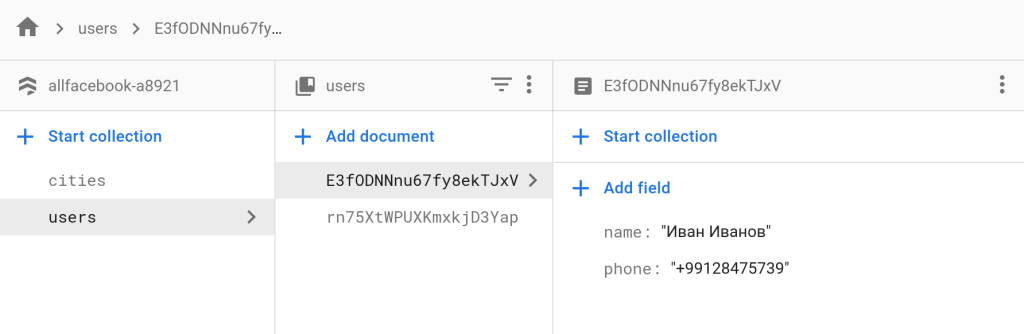
Create a new collection. For example, "Users". Now let's proceed to fill the collection with documents. I'm creating a user with "name" and "phone" fields to store the name and phone number respectively. Don't forget to specify the ID. The document identifier must be unique.
Integration with Dialogflow
Integration with the database is done through Fulfillment. I'll use the Inline Editor for simplicity. The database, server-side, and files will be stored in Google's cloud.
Here's an example code for Firebase initialization:
admin.initializeApp(functions.config().firebase);
const db = admin.firestore(); For writing data, use this code:
var name = agent.context.get('waitdata').parameters.name;
var phone = agent.context.get('waitdata').parameters.phone;
return db.collection('users').add({
name: name,
phone: phone
})
.then(function(docRef) {
agent.add('Thank you, ' + name + ', a manager will contact you in 30 minutes.');
})
.catch(function(error) {
agent.add('Error!');
});
}And for reading data:
return db.collection('cities').doc('1').get().then(function(document) {
var dt = document.data();
var dt_str = 'City: ' + dt.name + ' | ' + dt.code;
agent.add(dt_str);
});
}For data filtering, you can use where:
var query = userRef.where("name","==","Alex");More information can be found in the official documentation of Cloud Firestore.